As our reliance on technology continues to deepen, the importance of understanding and mitigating cybersecurity threats has become a top priority. In this article,
we will explore the various types of cybersecurity threats, their impact, and the countermeasures necessary to protect our digital assets.”
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/security/what-is-threat-prevention.html

What is Cybersecurity Threats
In today’s interconnected world, the threat of cyber attacks has become a major concern for individuals, businesses, and governments alike. Cybersecurity threats refer to the various types of attacks or unauthorized access to digital systems, networks, and data. These threats can come from a wide range of sources, including hackers, nation-states, organized crime groups, and even insider threats. The motivations behind these attacks vary, but common goals include financial gain, intellectual property theft, political espionage, and disruption of critical infrastructure.
Types of Cyber Attacks
Here are some popular categories of cyber attacks:
1.Malware Attacks:
- Viruses: Malicious software that attaches itself to a legitimate program and spreads
when that program is executed. - Worms: Self-replicating malware that spreads across networks without user
interaction. - Trojans: Malware disguised as legitimate software, which often tricks users into
installing it.
2.Phishing Attacks:
- Phishing: Deceptive attempts to obtain sensitive information (such as usernames,
passwords, or financial details) by posing as a trustworthy entity in electronic
communication.
3. Denial-of-Service (DoS) and Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) Attacks:
- DoS: Overloading a system, service, or network to disrupt its availability.
- DDoS: Coordinating multiple systems to flood a target with traffic, overwhelming its
resources.
4.Ransomware Attacks:
- Ransomware: Malware that encrypts a user’s data and demands payment (usually in
cryptocurrency) for its release.
5.SQL Injection:
- Exploiting vulnerabilities in a web application’s database by injecting malicious SQL
code, potentially gaining unauthorized access to the database.
6.Cross-Site Scripting (XSS):
- Injecting malicious scripts into web pages viewed by other users, often to steal
sensitive information.
7.Drive-by Downloads:
- Automatically downloading malicious software onto a user’s device when they visit a
compromised or malicious website.
8.Credential Stuffing:
- Using previously stolen usernames and passwords to gain unauthorized access to
multiple accounts, exploiting the tendency of users to reuse passwords.
9.Social Engineering Attacks:
- Manipulating individuals into divulging confidential information through
psychological manipulation.
10.IoT-Based Attacks:
- Exploiting vulnerabilities in Internet of Things (IoT) devices to gain unauthorized
access or launch attacks.
Data Encryption and Privacy
Data Encryption:
- Encryption is the process of converting plaintext data into unreadable ciphertext to protect it from unauthorized access.
- Encryption algorithms use keys to scramble and unscramble data, ensuring only authorized parties can access it.
- Types of encryption include:
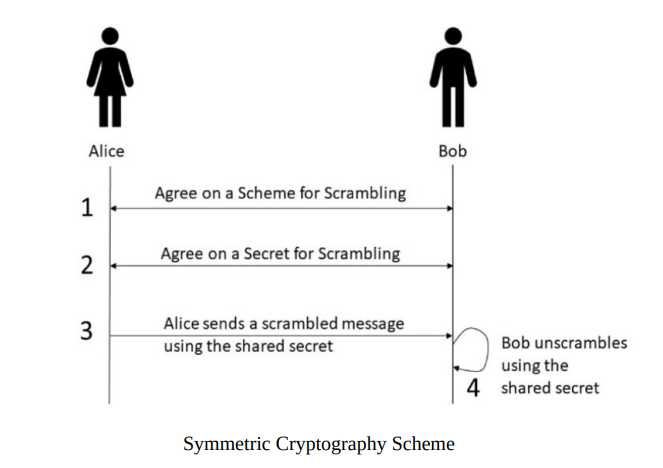
1.Symmetric cryptography
Symmetric cryptography, also known as secret-key or private-key cryptography,
is a form of encryption where the same key is used for both the encryption of
the plaintext and the decryption of the ciphertext.
Here’s how symmetric cryptography works:
- Key Generation: Two parties who wish to communicate securely must first agree on a
secret key. This key is then used for both encryption and decryption. - Encryption: The sender uses the shared secret key to encrypt the plaintext message, turning
it into ciphertext. The encryption algorithm and the key are kept secret. - Transmission: The ciphertext is sent over the communication channel.
- Decryption: The recipient uses the same secret key to decrypt the received ciphertext,
transforming it back into the original plaintext.
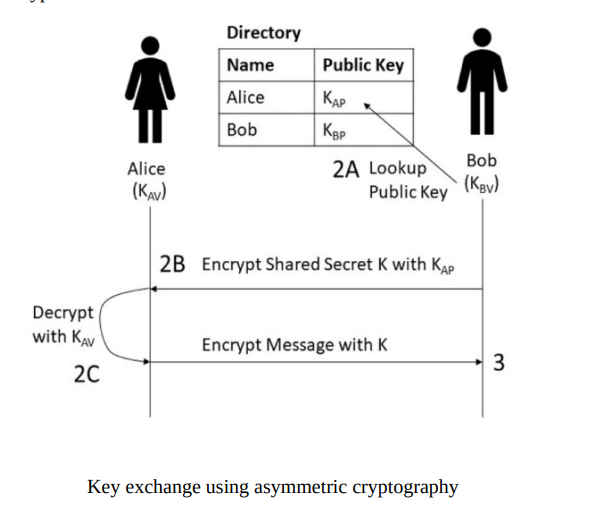
2.Asymmetric cryptography
Asymmetric cryptography, known as public-keycryptography,is a cryptographic system that
uses pairs of keys: public keys, which may be disseminated widely, and private keys, which are
known only to the owner.
3.Hashing
Common cryptographic hash functions include SHA-256 (Secure Hash Algorithm 256-bit), SHA-3,
and MD5 (Message Digest Algorithm 5).
However, MD5 is considered insecure for cryptographic purposes due to vulnerabilities,
and it is recommended to use stronger hash functions like SHA-256
for security-critical applications.
Cybersecurity Governance and Compliance
Cybersecurity Governance:
- Refers to the overall management and oversight of cybersecurity within an organization.
- Ensures cybersecurity is integrated into the organization’s overall strategy and risk management framework.
- Involves defining roles, responsibilities, and policies for cybersecurity.
Compliance:
- Refers to adhering to relevant laws, regulations, and industry standards for cybersecurity.
- Examples include GDPR, HIPAA, PCI-DSS, and NIST Cybersecurity Framework.
- Involves implementing controls and procedures to meet compliance requirements.
Threat Intelligence and Vulnerability Management
Threat Intelligence:
- Refers to the process of gathering and analyzing information about potential threats.
- Helps identify and understand threat actors, their motives, and tactics.
- Enables organizations to anticipate and prepare for potential attacks.
Vulnerability Management:
- Identifies, classifies, and prioritizes vulnerabilities in systems and applications.
- Involves remediating or mitigating vulnerabilities to prevent exploitation.
- Helps reduce the attack surface and minimize risk.
Key aspects:
- Threat Intelligence:
- Data collection and analysis
- Threat modeling and prediction
- Incident response planning
- Vulnerability Management:
- Vulnerability scanning and assessment
- Prioritization and remediation
- Patch management and configuration
Cybersecurity Awareness and Training
Cybersecurity Awareness:
- Involves educating users about cybersecurity risks and best practices.
- Helps individuals understand their role in preventing cyber attacks.
- Covers topics like password management, phishing, and online safety.
Key aspects:
- User education and awareness programs
- Phishing simulations and testing
- Security ambassadors and champions
Cybersecurity Training:
- Provides hands-on training and simulations to develop cybersecurity skills.
- Covers topics like incident response, threat analysis, and security frameworks.
- Helps organizations develop a cybersecurity-savvy workforce.
Key aspects:
- Role-based training and certification
- Simulation-based training and exercises
- Continuous learning and development
Password Management and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Password Management:
- Securely stores and generates complex passwords.
- Automatically fills in login credentials.
- Alerts users to password weaknesses and expirations.
Key aspects:
- Password generation and storage
- Auto-fill and password rotation
- Security alerts and reporting
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA):
- Adds additional verification steps beyond passwords.
- Uses factors like:
- Something you know (e.g., PIN, password)
- Something you have (e.g., smart card, token)
- Something you are (e.g., biometric, face recognition)
- Increases security and reduces risk of unauthorized access.
Key aspects:
- One-time passwords (OTPs) and SMS codes
- Authenticator apps and smart tokens
- Biometric and behavioral authentication
Firewall Configuration and Network Segmentation
A firewall is a crucial security technology that acts as a barrier between a trusted internal network and untrusted external networks,
such as the internet.
Firewall Configuration:
- A firewall is a network security system that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules.
- Configuring a firewall involves setting up rules to allow or block traffic to specific ports, IP addresses, and protocols.
- This helps prevent unauthorized access, blocks malicious traffic, and hides internal IP addresses.
Network Segmentation:
- Network segmentation involves dividing a larger network into smaller, isolated segments or subnets.
- Each segment is isolated from the others, reducing the attack surface and preventing lateral movement in case of a breach.
- Segmentation can be done using VLANs, subnets, firewalls, or other technologies.
Together, firewall configuration and network segmentation provide a strong defense against cyber threats, helping to:
- Prevent unauthorized access
- Reduce the attack surface
- Limit the spread of malware
Penetration Testing and Ethical Hacking
Penetration Testing (Pen Testing or Pentesting):
- Simulates a cyber attack on a computer system, network, or web application to test its defenses.
- Identifies vulnerabilities and weaknesses, providing a vulnerability assessment.
- Helps organizations strengthen their security posture and protect against threats.
Ethical Hacking (White-Hat Hacking):
- Involves authorized attempts to exploit vulnerabilities and weaknesses.
- Conducted by security professionals (white-hat hackers) to help organizations improve their security.
- Goals include:
- Identifying vulnerabilities
- Developing exploits
- Improving security measures




Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.